ACE Inhibitor (ACE-I) induced cough
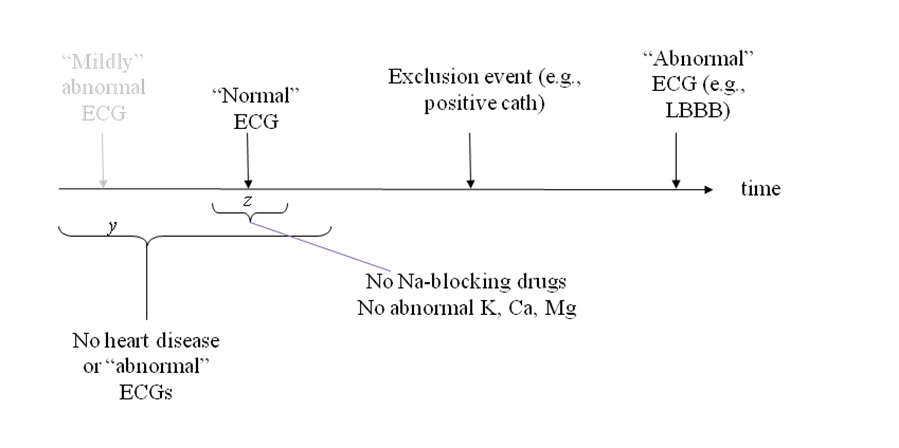
ACE-I induced cough is a common side effect of use of ACE inhibitors, one of the most common class of antihypertensives. The frequency of ACEI-induced cough varies based on ancestry. A GWAS of ACEI cough using this algorithm in the eMERGE Network identified KCNIP4 as associated with this phenotype, which was validated in two replication cohorts.
Cases are those with ACEI cough. Controls are those exposed to ACEI without adverse events noted and not switched to angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Algorithm validated - December 12, 2012.