Final
Febrile Neutropenia (Pediatric)
Background: Febrile neutropenia (FN) is a serious complication of myelosuppressive chemotherapy, defined by fever occurring in the context of neutropenia. Prompt recognition and treatment are essential to reduce morbidity and mortality. This algorithm focuses on "high-risk" FN as defined in the ‘Early versus Late Stopping of Antibiotics in high-risk FN’ (ELSA-FN) randomised control trial as expected absolute neutrophil count (ANC) <500 cells/mm3 for ≥7 days.
Functional seizures
Algorithm to detect functional seizures, also known as:
Psychogenic nonepileptic seizures
Nonepileptic attack disorder
Pseudoseizures
Hystero-epilepsy
Conversion disorder with seizures
Dissociative Seizures
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Phenotype Algorithm
HbA1C
This is the PRIMED Consortium algorithm to obtain a single Hba1c value per individual to use in analyses. Here is the overall procedures:
Hearing Loss
Phenotype Description: individuals with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL)
Below are algorithms used to identify individuals with SNHL at BioVU. If you have questions regarding any of the information presented on this page, you may contact either:
Wei-Qi Wei at wei-qi.wei@vanderbilt.edu or Joshua Denny at josh.denny@vanderbilt.edu
Height
Algorithm to select patients with height measures unaffected by environmental factors (i.e. diseases & medications) that can cause an abnormal change in height. Comprehensive documentation of the algorithm can be found here on this PheKB page. Similar to our T2DM algorithm, you can install an executable version of the algorithm implemented as workflows for the Konstanz Information Miner (KNIME) data mining tool.
Herpes Zoster
Herpes zoster, also known as zoster or shingles, is caused by a virus called varicella zoster virus (VZV). Initial infection with the virus causes chickenpox. After chickenpox resolves the virus continues to resides in certain nerve cells. It may remain latent for many years. It may also re-activate, many years later, and cause shingles which is a painful skin rash. How the virus remains latent in the body is not well understood.
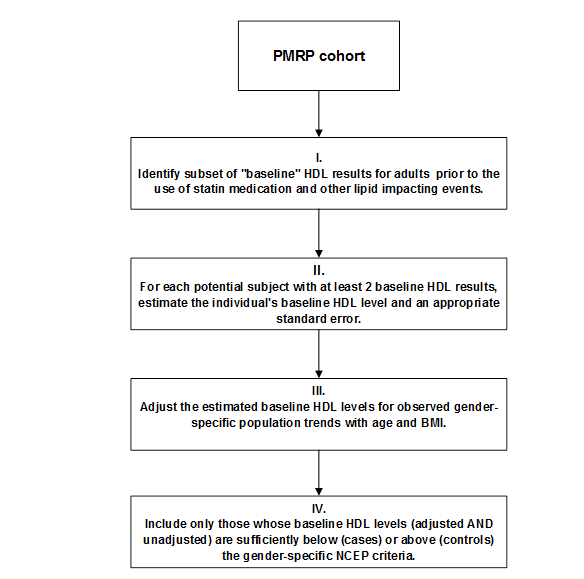
High-Density Lipoproteins (HDL)
Algorithm to identify patients with low levels of high-density lipoproteins (HDL).
FLOWCHART of HDL Phenotyping Process